What Are Silos Used For
As companies re-evaluate current Information technology infrastructures and processes with the goal of creating more efficient, resilient, and intuitive enterprise systems, one affair has become very clear: traditional data warehousing architectures that separate information storage from usage are pretty much obsolete.
The basic structure of current data platforms inhibits strategic outcomes past creating data silos and inconsistencies in dashboards and reports across an system. As a issue, the quality of the data is often questionable since information technology is an amalgam of information from multiple sources. The pattern disadvantages and limitations of these platforms include:
- Redundant layers in the architecture and multiple data marts that result in increased processing time and information latency.
- Complexity in the data flow and the existing processing layers that make it cost-prohibitive to optimize or scale the performance of the hardware and software that comprise these systems.
- The need for multiple data marts and independent data repositories due to the absence of a single user-based consumption layer.
- An disability to support enabling information science technologies such as predictive modeling, AI, and machine learning that are future drivers of digital transformation.
- Antiquated identity, security, and audit controls that escalate risks to the enterprise.
Since information is an anchor point for the digital transformation efforts at every company, it makes sense to create a modern data platform that can support real-time processing and enabling technologies like AI, while offering a future-proof architecture that can deliver actionable business intelligence to achieve an organization's goals.
This is exactly what we did at CareSource, ane of the nation'due south largest Medicaid managed care plans, serving more than two million members beyond 5 states. Our goals included enabling seamless access to medical records; easily sharing medical information with members and health care providers throughout the network; and supporting new service offerings such as remote intendance.
We took it a step farther in reimagining and re-architecting this platform by creating a tightly integrated data textile that allows agile, efficient, and secure data movement within CareSource and with our partners to enable transparency and interoperability for our providers, members, community, and government organizations. In outcome, this integration creates a information supply chain that makes it easy to notice, access, and consume information, thereby establishing a cost-constructive unmarried source of truth.
 CareSource
CareSource Diving into data compages
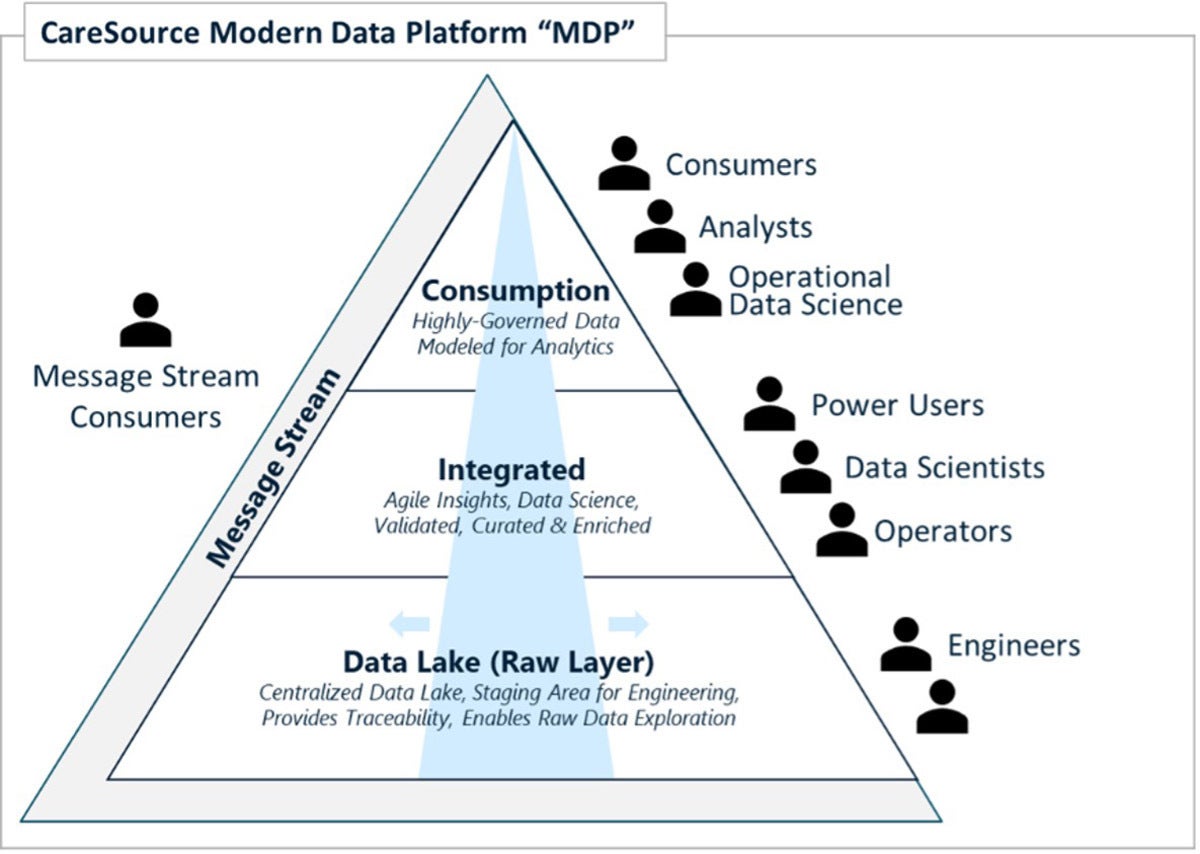
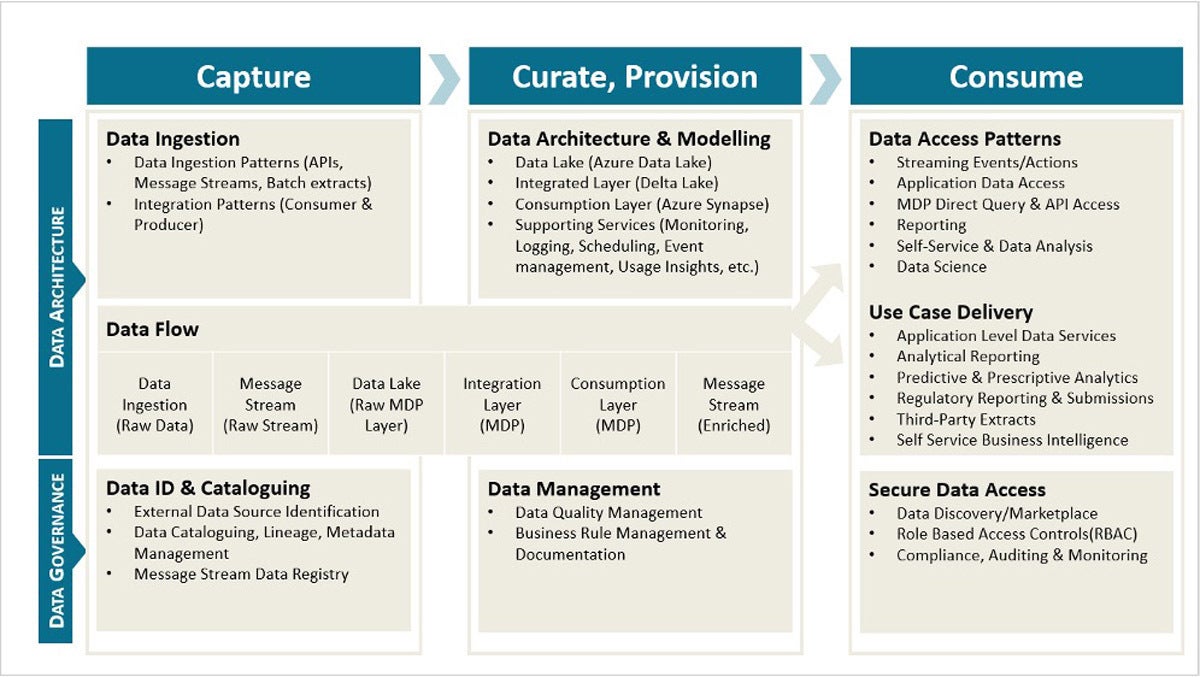
CareSource's mod information platform is a fully cloud-based solution that replaces an on-premises enterprise information warehouse and many other siloed reporting databases and is the key hub for all information needs across the organization. In one case completed, the platform will host and manage 40TB of data with almost real-time data movement supporting 700 to 1,000 users (data consumers, data analysts, and advanced analysts), and producing more than 1,500 prebuilt reports/dashboards.
Data is ingested in a raw format in the data lake and is and then processed and refined through a data hub and enriched into a course ready for consumption in the data warehouse. Each layer of the architecture supports concern-driven operational (transactional and regulatory) and analytical use cases.
Data governance was another primal aspect in the pattern of this mod data platform, with principles and practices integrated into each layer of the architecture. The objective was to create an overarching umbrella that would enable a high-level of trust in the data accessed by concern users to make decisions.
 CareSource
CareSource An eye on outcomes
Successfully planning and developing a governance construction for a data architecture requires the active involvement of IT and business concern every bit co-owners and co-leaders of the endeavor. In our example, that collaboration consisted of participating in several development coordination groups, including a data governance executive steering committee, a information governance function, a information governance quango, an executive data steering commission, and data stewardship, informational, and consumer committees.
Some primal points to consider in launching and guiding such an initiative:
- Focus on enabling business outcomes. Although technology and IT apparently play fundamental roles in driving and executing the project, the focus is not on IT, but on the overall objective to enable business organisation outcomes and priorities. As such, the unabridged executive leadership, or C-suite, serves as the oversight and governing trunk of the program, as part of the executive information steering committee, in providing back up and direction.
- Continue business team members and leaders educated and informed. Scheduling demos with each iteration sprint gives these stakeholders an opportunity to provide feedback and recommendations.
- Have a use case-driven approach. This volition assistance conspicuously frame business organisation objectives and avoid rabbit holes. At CareSource, nosotros were as well intentional in our definitions of the guiding principles effectually price models, especially in applying new technologies and platforms, to avoid defoliation around upkeep responsibilities and expenditures.
- Make employ of manufacture-standard information models related to speed of delivery and integration of new sources of data. We integrated such a model across different subject areas, allowing for improved ease in finding and consuming data, as well as creating and generating consolidated reporting.
Finally, remember that information governance needs to be metrics driven. Information technology is important to conspicuously lay out how the different data governance councils, in both IT and concern, work with each other to go the work done and make decisions. Functional roles and responsibilities should be established and understood to create the capacity to engage and do the work.
In setting upward the data governance programme, we recommend the executive data steering committee too be fabricated upwards of senior staff members who meet regularly. The functional roles for all data governance bodies are built into the roles and responsibilities, and capacity is created to successfully engage and exercise the work.
Angela McArthur is Senior Vice President of Information technology Data and Enterprise Services , and Joy Mukherjee is Vice President, Enterprise Data Services at CareSource, a nonprofit, multi-land health plan recognized as a national leader in managed intendance. CareSource is a CIO Executive Council fellow member company.
What Are Silos Used For,
Source: https://www.cio.com/article/188810/how-caresource-ditched-its-data-silos.html
Posted by: glessnersopland.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Are Silos Used For"
Post a Comment